

Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-19 Origin: Site












Injection molding is one of the most influential manufacturing processes in today’s industrial landscape. By combining precision, efficiency, and versatility, it enables mass production of durable plastic components used in virtually every sector—from automotive and medical to consumer electronics and household products. Understanding how injection molded parts are designed, produced, and applied not only highlights their importance but also helps businesses make smarter decisions about materials, costs, and production strategies.
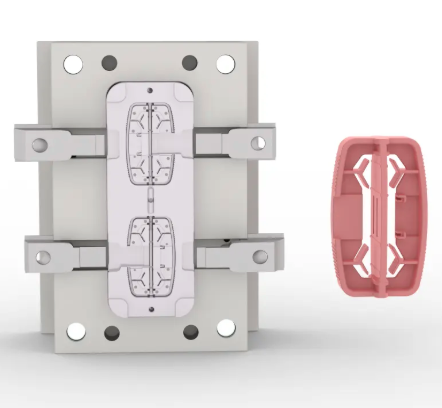
Injection molded parts are the backbone of modern manufacturing, representing a process where molten resin is injected into a precisely engineered mold cavity. This innovative method allows for the creation of high-volume plastic components that are not only strong and durable but also cost-effective and consistent in their dimensions and quality. The ubiquity of injection molded parts is a testament to their versatility and reliability; they can be found in a myriad of everyday items. From the car dashboard you touch every morning to the toothbrush handle you grip each night, and the electronics housings that encase the gadgets you rely on, injection molded parts play an integral role in our lives. Their applications span across industries, including automotive, medical, consumer goods, and technology, highlighting their indispensable nature in today’s fast-paced world.
The world of injection molding is diverse, offering a range of mold types designed to meet specific production needs:
Single-cavity molds – These molds are designed for efficiency, producing one part per cycle. They are ideal for low to medium volume production runs where the focus is on quality and precision rather than high output.
Multi-cavity molds – In contrast, multi-cavity molds are engineered to produce multiple parts simultaneously, significantly increasing production rates. This type of mold is perfect for high-volume manufacturing where speed and cost-efficiency are paramount.
Family molds – These molds offer the flexibility to produce different parts in a single shot. This is particularly useful for manufacturers who need to produce a variety of components that share similar features or dimensions.
Hot runner molds – Equipped with a system that keeps the material molten even after the injection phase, hot runner molds minimize material waste and improve overall efficiency. They are a popular choice for manufacturers looking to reduce costs and environmental impact.
Cold runner molds – These molds use a simpler design where the material cools in the runner system, resulting in more material waste. However, they are more affordable to produce and maintain, making them a viable option for smaller production runs or when part design changes are frequent.
The choice of mold material is a critical decision that impacts the longevity, performance, and cost of the mold:
Steel molds – Known for their durability and resistance to wear, steel molds are the go-to option for high-volume production. They offer a longer lifespan and maintain precision over time, making them a cost-effective solution in the long run.
Aluminum molds – These molds are favored for their speed of production and lighter weight. However, they wear out more quickly than steel molds, making them more suitable for lower-volume production or for parts that require frequent design changes.
The decision between steel and aluminum molds should be based on a careful evaluation of your production volume, part complexity, and budget constraints. Each material has its advantages and is best suited to different scenarios, ensuring that manufacturers can tailor their mold selection to their specific needs.
The process of creating injection molded parts is a meticulous journey that transforms a concept into a tangible product. Here’s a detailed look at each step involved in this manufacturing process:
The initial phase begins with defining the part’s function and requirements. This involves creating detailed specifications that outline the part’s dimensions, tolerances, and performance criteria. Designers use CAD software to translate these specifications into a 3D model, which serves as the blueprint for the part.
Choosing the right resin is crucial as it determines the part’s properties. Materials are selected based on their strength, durability, heat resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Common choices include polyethylene, polypropylene, and ABS, each offering unique characteristics suited to different applications.
Before full-scale production, a prototype is created to validate the design. This step allows for testing the part’s functionality and identifying any design flaws. Prototypes can be made using various methods such as 3D printing or CNC machining, providing a physical model to refine the design.
This critical phase involves designing the mold that will shape the molten resin into the desired part. Mold design considers factors like parting lines, ejection systems, and cooling channels. Once the design is finalized, the mold is manufactured using precision machining techniques, often from steel or aluminum.
The heart of the process, injection molding involves heating the resin until it becomes molten and then injecting it into the mold cavity under high pressure. The mold is cooled to solidify the part, which is then ejected once it has reached the required strength.
After ejection, parts may undergo post-processing to refine their appearance and functionality. This can include trimming excess material, polishing surfaces for a smoother finish, or painting for aesthetic purposes. Post-processing ensures that the parts meet the desired quality standards.
The final step involves rigorous quality control measures to ensure that each part meets the specified requirements. Inspections check for accuracy in dimensions, strength, and finish. Quality control is essential for maintaining consistency and reliability in the production of injection molded parts.
By following these steps, manufacturers can ensure that the injection molded parts they produce are of high quality, reliable, and visually appealing, ready to meet the demands of various industries and applications.
| Defect | Cause | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Warping | Uneven shrinkage | Uniform wall thickness |
| Sink marks | Thick sections | Proper rib design |
| Flash | Mold misalignment | Better mold fit |
| Short shots | Incomplete filling | Adjust pressure, venting |
| Burn marks | Overheating | Control temperature, airflow |
The cost of making injection molded parts depends on:
Mold complexity – detailed features cost more.
Resin selection – engineering plastics raise costs.
Production volume – larger runs lower per-part cost.
Cycle time – shorter cycles save money.
Pro tip: Keep designs simple, choose cost-effective resins, and scale production for savings.
Injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process with a wide range of applications across various industries. The ability to produce complex shapes and intricate details in high volumes makes it indispensable for many modern products.
In the automotive sector, injection molded parts are ubiquitous. They contribute to both the aesthetics and functionality of vehicles. Dashboards, bumpers, and switches are common components produced through injection molding. These parts must meet stringent safety standards and durability requirements, making the precision of injection molding processes crucial.
The medical industry relies heavily on injection molding for the production of critical devices. Syringes, casings, and tubing connectors are often made using this method. The materials used must be biocompatible and sterile, highlighting the importance of material selection and the cleanliness of the injection molding process in medical applications.
Consumer electronics benefit greatly from injection molding, particularly for housings and cases. Phone cases, laptop housings, and other electronic enclosures are designed to be lightweight yet robust, protecting sensitive components from environmental factors and physical impacts.
Injection molding plays a significant role in the packaging sector, where it is used to create bottles, caps, and containers. These parts must be able to withstand the rigors of transportation and storage while also being visually appealing to consumers. The precision of injection molding ensures that packaging is both functional and aesthetically pleasing.

You need a 3D design, material choice, and a mold manufacturer.
Mold production may take 4–12 weeks. Once ready, each part is made in seconds.
Yes, many injection molding companies use recycled resins to cut cost and support sustainability.
Basic molds cost a few thousand dollars. Complex multi-cavity molds can exceed $50,000.
High-quality molds achieve tolerances around ±0.005 inches.
Injection molded parts have become the cornerstone of modern product design and manufacturing. With the right mold type, material selection, and production process, businesses can achieve cost-effective, high-quality, and scalable solutions that meet diverse industry needs. As technology advances and sustainability gains importance, injection molding will continue to evolve, driving innovation and shaping the products we use every day. Dongguan Quanhao Plastic Mold Co., Ltd., with its expertise in precision mold making and injection molding services, is committed to helping global clients bring their ideas to life through reliable, efficient, and innovative manufacturing solutions.